Email Deliverability: How to Get Emails in Customer Inboxes

Reading Time: 7 minutes
By 2023, the number of email users worldwide is expected to grow to 4.3 billion, which is half the world’s population. To capitalize on this, consumer brands spend hundreds of thousands of dollars on email marketing. But an email campaign is only successful if the intended audience opens, reads, and interacts with your communication. More often than not, consumers don’t even open emails that land outside their inboxes—which is what deliverability is all about.
What is email deliverability?
Deliverability tells you how many emails land in your user’s inbox instead of in their spam or junk folders.
“Spam is where emails go to die.”
-Sadikshya Pant, Senior Email Deliverability Consultant, MoEngage
Spam is a serious problem worldwide. Gmail noted that 50% of the 293 billion emails sent daily in 2019 were tagged as spam. 70% of these were marketing content, which means 102 billion marketing emails fade into digital oblivion each year.
Some of your users won’t even know that a spam or trash folder exists. And most of the ones that do, never check their spam folders. To make things worse, ISPs (Internet Service Providers) flag reported emails as suspicious. These emails end up having their links and images deactivated.
How deliverability is different from email delivery
Email delivery is not the same as deliverability. Delivery measures the number of emails received by the user. Deliverability measures how many delivered emails land in the inbox folder.
For example, consider an email campaign targeting 100 users, with 98% delivery and 60% deliverability. This means that 98 out of 100 users received the emails, but only 60 received the email in their inbox folders. The remaining 40 probably deleted or ignored the emails because they landed up in the wrong folder.

Scale these numbers by a factor of a few thousand or more, and the importance of deliverability becomes clear.
Factors impacting email deliverability
Unfortunately, ISPs don’t share information about which folders emails land in, be it spam, junk, or any of the subfolders in a user’s inbox (Primary/Promotions/Updates). Even so, you can deduce deliverability based on factors like:
1. Domain/IP Reputation
Domain and IP reputations directly affect email engagement because email service providers measure domain/IP reputation to decide which folder to put an email in. One sure-shot way to improve domain reputation is via list management.
| List management tip:
Clean your email lists regularly to maintain good domain and IP reputations. Remove or decrease mailing frequency for disinterested users. Identify hard bounces, spam traps, and blacklists early on. Keep your email list populated with only those users that want to receive your emails. |
2. Performance Metrics and User Engagement
ISPs use performance metrics like opens, clicks, unsubscribes, or spam complaint rates to decide whether to accept or reject emails from a sender. This also helps them decide where to place the accepted emails (Spam/Promotions/Updates folders).
Positive user engagements include:
- Opening/clicking an email
- Reading an email thoroughly or opening it multiple times
- Replying, forwarding, or marking an email
- Bookmarking the sender or adding to their address book
- Moving emails to the primary inbox folder
Negative user engagements include:
- Marking or reporting emails as spam
- Deleting or ignoring emails without interacting
- Sweeping or blocking the sender
Negative engagement impact deliverability and take a lot of time to recover from. But marketers can adjust their strategy to address negative engagements and increase positive engagements.
Best practices to deliver emails to your user’s inbox
All ISPs have independent policies for acceptable email practices, but many of them share common concepts you can practice for better inbox placement.
1. Sender Authentication
All ISPs have multiple authentication protocols to verify that the sender is the brand they claim to be. ISPs tend to be wary of spammers, so failing basic authentications could result in having the emails rejected, blocked, or flagged as spam. When sender authentications fail, both delivery and deliverability take a hit.
2. Clean User Collection

Always employ organic user collection methods — never purchase an email list. Most users in purchased email lists turn out to be invalid. The rest might report your email as spam or unsubscribe. This skews deliverability data and affects domain reputation.
There are several clean ways to build user lists organically:
- Incentivize sign-ups via referral programs or promotions.
- Promote your brand via third-party websites or apps to build trust.
- Introduce loyalty programs or memberships.
- Collect email addresses through the use of your products or services; make sure email ids are valid.
Clean acquisition methods set reasonable expectations for customers about their experience and give them an option to bow out if they don’t enjoy the content.
3. Legal Compliance for Deliverability
All countries have independent mailing laws that protect their users’ rights to privacy and quality of experience. Complying and being up-to-date with new or revised laws specific to a user’s location will help avoid hefty lawsuits.
4. Segmentation and Optimal Send Frequency
Think about the last time you unsubscribed from a promotional email. It was probably because of irrelevant product suggestions or annoyingly frequent emails from a brand you purchased from long ago.
Emailing people too often irritates them, and emailing too infrequently doesn’t build brand recognition. It’s important to find out the optimal send frequency for your customer, i.e., the perfect number of emails a customer would want to receive without adverse reactions. Finding this is an iterative process, and it doesn’t work the same way for all your customers.
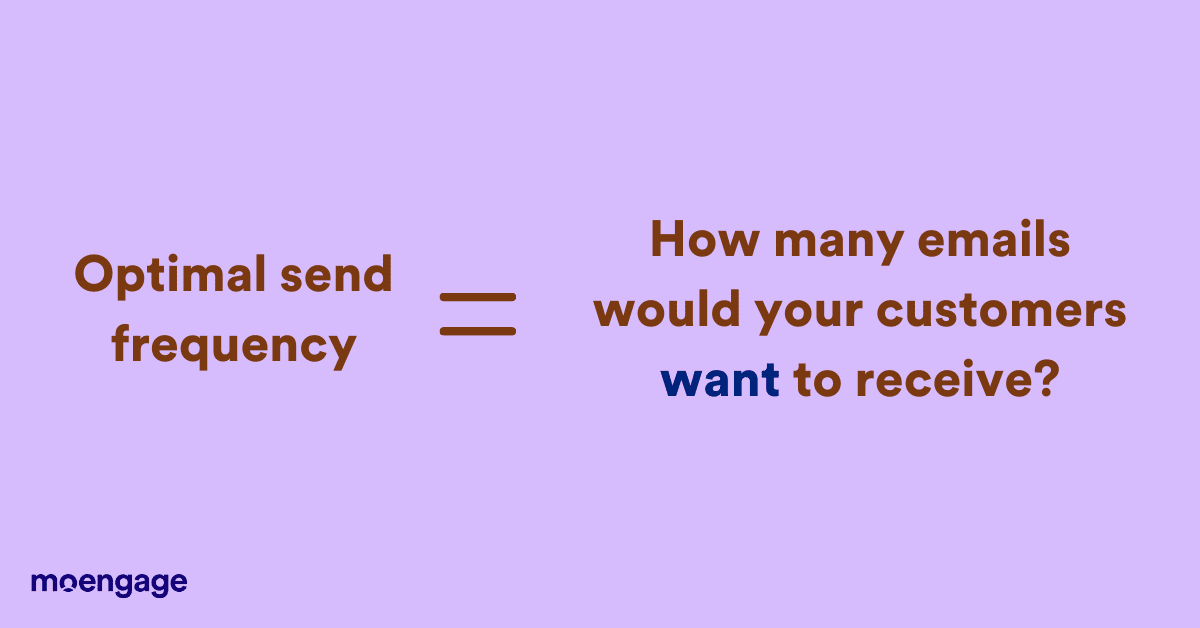
This neatly brings up the topic of segmentation, i.e., the categorization of users based on overlapping criteria. Users love preferential treatment—a ‘one-size-fits-all’ package doesn’t work. It’s crucial to segment your users based on their previous buying cycles, upcoming relevant events, locations, and frequency of website visits.
With tools like MoEngage, you can categorize your emails into dynamic segments based on their behavior—and adjust mailing frequency accordingly. Engaging users at the right time with the most relevant content makes for a personal experience that goes beyond their expectations, fostering goodwill and investment in the brand.
Here are a few ways to segment users:
- Run event-based trigger campaigns and target customers based on products viewed, purchased, added to cart, or more.
- Create post-purchase engagement campaigns like product review requests a few days after delivery, followed by personalized email recommendations on bundled or related products or custom codes for future purchases.
- Collect personal details after a sign-up and use this to personalize your communication.
5. Sunsetting for Better Deliverability
A marketer’s worst nightmare is getting emails flagged as spam, leading their domain reputation and resources to take a hit. Sunsetting is a strategy that keeps user lists clean by removing inactive and stale users. ISPs turn inactive email addresses into spam traps (inactive email addresses used to trap spammers), which cause list qualities to degrade, further affecting performance metrics and deliverability data.
Use reactivation campaigns to bring back inactive users (by adjusting email frequency, content, or trying different channels), but lost causes should be promptly acknowledged and dealt with accordingly.
6. Automated Removal of Bad Actors
While sunsetting focuses on retiring users based on their activity, some users, a.k.a. bad actors (hard bouncers, unsubscribers, and spam reporters), are to be removed immediately. This will prevent any subsequent actions that will affect reputation.
It’s essential to give your users an easy exit mechanism. Make your ‘unsubscribe’ button prominent and provide an uncomplicated exit journey if they desire it.
7. Personalization
True to the modern consumer mindset, people love tailored content suited to their needs. Content unique to each user leads to higher email open rates, clicks, replies, forwards, and conversions.

Here are some basic methods to help you personalize your emails:
- A compelling subject line that isn’t misleading: Nothing causes a user to reach for the unsubscribe button faster than an intriguing subject line that’s deceiving and irrelevant to the email’s content.
- Clear, consistent information: Ensure your sender’s name, email address, subject line, and preheader text reflect your brand’s identity. Vital information like the terms and conditions and privacy policies should be made clear.
- A direct call to action: Nudge customers towards taking a desired action, whether reading that Mother’s Day newsletter or taking advantage of a limited offer, by enforcing clear call-to-actions and a streamlined email design.
- Compatibility across platforms and devices: Check that all your emails render as intended across different devices and platforms; otherwise, you risk irritating the user.
- Brand conformity: Maintain brand aesthetic across consecutive emails to build on the customers’ subconscious. Add contact information to establish the brand as a physical entity that’s easily reachable.
8. Understanding spam filters
All ISPs have a content scanner that scans emails for spam-like characteristics and filters them. These are the basic rules to ensure your emails aren’t categorized as spam:
- Don’t create image-heavy emails: A 40:60 text-to-image ratio is considered good.
- Maintain standard template sizes: The standard HTML email template size is 600 pixels for desktops, 320 pixels for vertical, and 480 pixels for horizontal views on mobile devices.
- Keep it crisp: Emails should be smaller than 102 kB, or Gmail will hide the content behind a “View entire message” link.
- Use alt tags: Alt tags should be added for images so that they display text in case the images don’t render.
- Avoid spammy subject lines, special characters ($$$), and token “spam keywords” (“F R E E” or “This is not a scam”) that could trigger a spam filter. Here’s a list of spam keywords to avoid.
- Use reputed image hosting services like Amazon AWS or Cloudflare for better security, faster load times, and additional borrowed authenticity.
- Keep your HTML code light and clean without any hidden images or URLs.
9. Google Annotations
Sophisticated ISPs like Gmail analyze user engagements in real-time to sort relevant marketing emails into the ‘Promotions’ tab of the inbox. Use Google Annotations to highlight emails for more user interactions and get bumped up to the ‘Updates’ tab.
10. Monitoring Ongoing Sends
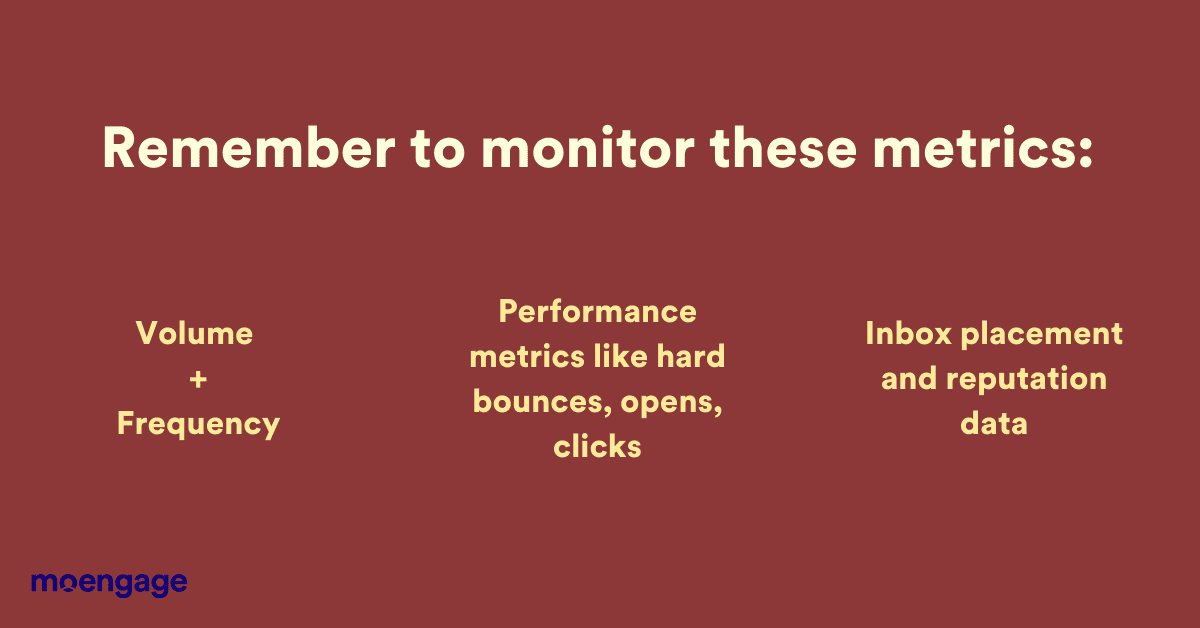
Create a system to ensure all your marketing strategies coalesce and work with each other. Monitor these trends and metrics:
- Volume trends: Volume trends usually tend to be gradual. Sudden spikes in volume and frequency of emails are indicative of abnormal activity. If left unaddressed, they will affect user interaction.
- Performance metrics: Unusual trends in hard bounces, opens, clicks, spam complaints, unsubscribes, spam traps, blocklists, and blacklists adversely affect deliverability.
- Reputation data: Monitor your inbox placement data through third-party applications like eDataSource, ReturnPath, or 250ok, and address any abnormalities immediately.
Conclusion
Achieving successful email deliverability is arduous and rarely ever straightforward. It’s essential to invest in a good email deliverability consultancy that can tell you what’s working and what’s not—and how to improve deliverability with actionable insights.
At MoEngage, we offer deliverability consultancy services which include setting up proper authentications, email strategy discussions, assistance with inbox placement/bulking issues, troubleshooting blogs and blacklisting issues, content analysis, and reviewing industry best practices. We’ll also help you implement new features like BIMI or Google Annotations to establish your brand authenticity.







