RFM Segments Based on RFM Analysis: An In-Depth Guide [Updated]
![RFM Segments Based on RFM Analysis: An In-Depth Guide [Updated]](https://www.moengage.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/predictive-segments-using-rfm-moengage-3.jpg)
Reading Time: 11 minutes
This blog on RFM analysis is a definitive step-by-step guide to understanding the Segmentation and Analysis involved in RFM Modelling and its practical applications, helping you better serve customers and maximize customer lifetime value.
What Does RFM Mean?
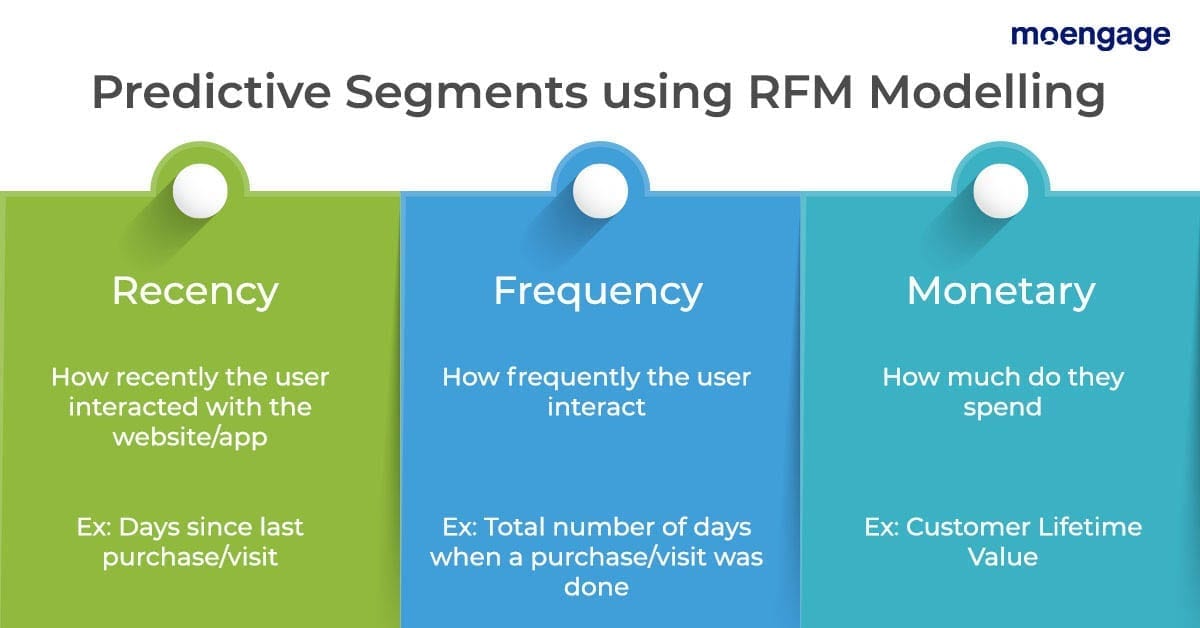
The RFM model of customer value uses proven marketing principles to help businesses differentiate between marketing to existing and new customers and helps them create relevant and personalized messaging by understanding user behavior.
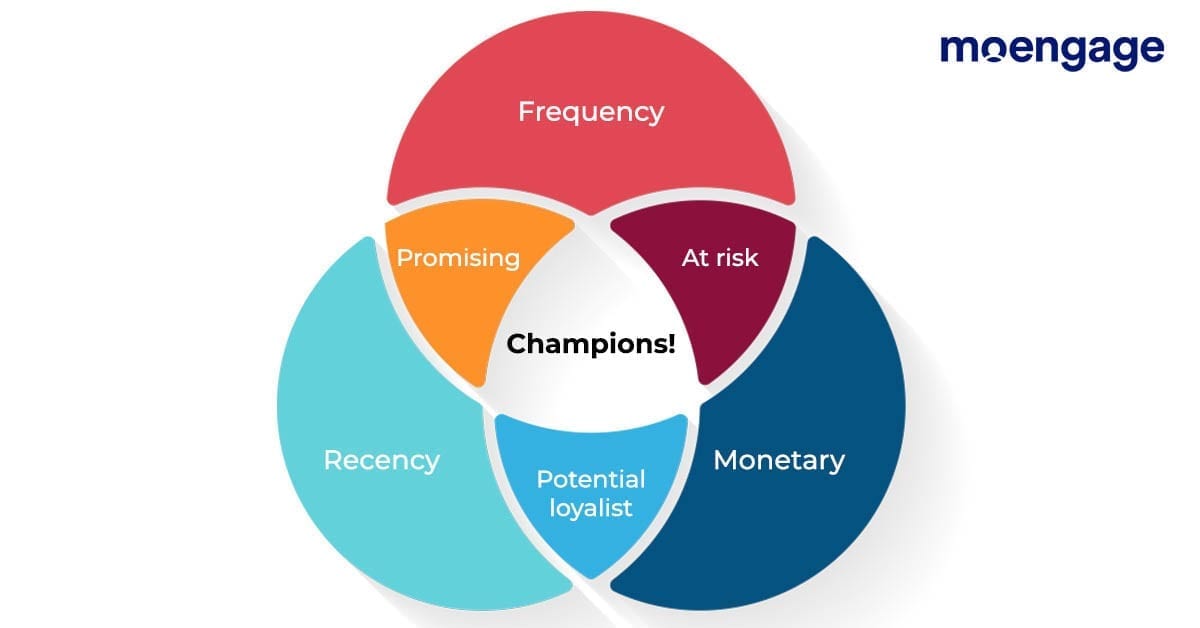
The RFM analysis model allows the business to segment its customers based on three criteria based on an existing customer’s transaction history, namely:
Recency (When Was The Last Time Your Customer Purchased a Product/Service?)
In RFM analysis, R stands for Recency.
A high recency score means a customer has positively considered your brand for a purchase decision recently. Recency can be scored by grading on custom-built filters such as bought on the last 7 days/1 month/3 months and so on, depending on the nature of the business.
Frequency (How Often Did The Customer Purchase in a Year/Fixed Time Period?)
F stands for Frequency in RFM analysis.
A high-frequency score means a customer buys your brand frequently and is likely to be a loyalist of your brand. To calculate frequency, businesses need to analyze the total number of purchases completed by customers in a fixed time period. Frequency can be scored by grading on custom-built filters such as bought thrice in a year/bought once a month and so on, depending on the nature of the business.
Monetary Value (How Much Money Has the Customer Spent on Your Brand So Far?)
Lastly, the M in RFM analysis stands for Monetary Value.
A high monetary value score means a customer is the highest purchase history of your brand. Monetary value score can be graded on custom-built filters like spent more than Rs.10,000/30,000/50,0000 and so on, depending on the nature of the business.
All the above criteria can be graded on a scale of 1 to 5, with 5 being the best score you could assign a customer. It is also critical to specify an appropriate range for each grade, in order to create a customer group with a similar or a particular behavior.
Why is RFM Analysis Better than Traditional Segmentation Methods?
The RFM analysis model is built on transactions between the customer and the business, to create a robust data-backed method based on hard numbers. This customer data is graded, further analyzed, and then segmented in order to engage customers as distinct groups. This model helps businesses effectively analyze the past buying behavior of each customer, to predict and shape future customer behavior.
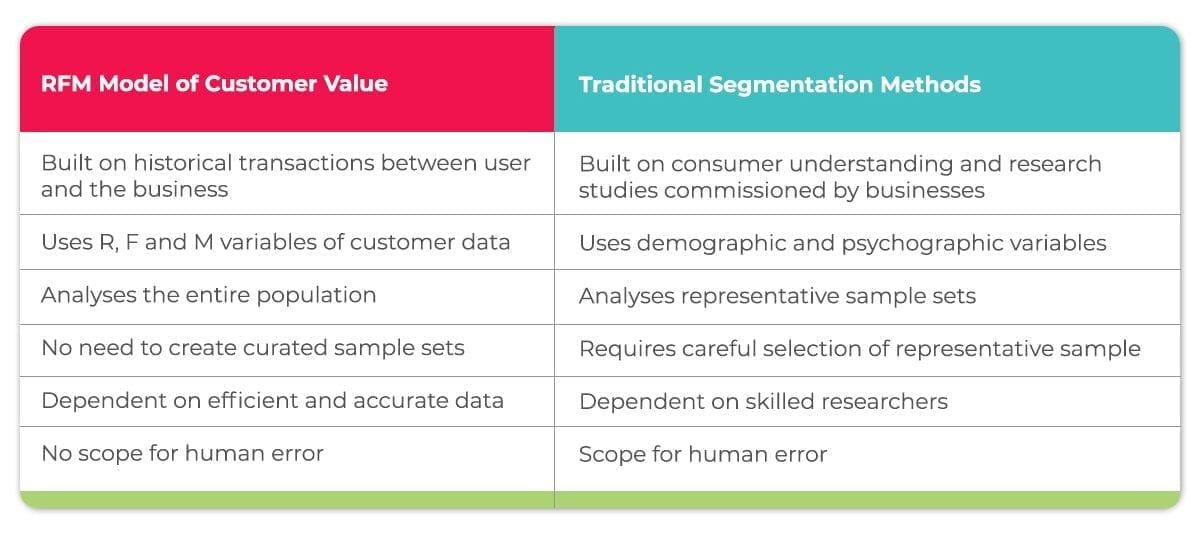
Traditional methods of customer segmentation, used by market research companies before the advent of data analytics, used variables like demographic and psychographic factors to group their customers. Researchers always utilize sample audiences to predict population behavior, which reduces market researchers’ ability in predicting future customer behavior of niche customer groups.
These studies are carried out manually, are dependent on skilled researchers, and are prone to human error. A sample could be incorrect, due to many reasons like an insufficient number of consumers, incorrect gender balance, varying psychographic factors, etc.
These problems cannot occur in RFM analysis, as it is a fundamentally data-centric model which analyses the entire population set, instead of a curated sample set. In addition to that, the variables of the RFM model are 100% accurate and precise, whereas traditional research involved factors like psychographics, which could be interpreted subjectively.
The RFM model helps a business define interactions with each specific customer, creating opportunities to increase the relevance of messaging, and eventually creating the potential for increased customer lifetime value.
RFM analysis has the potential to create seamless interactions with high customer satisfaction, helping customers feel that the brand understands them and can effectively cater to their needs at all times.
How RFM Helps Improve Business Understanding
RFM modeling increases a business’ ability to prevent churn by using fundamental marketing principles of segmentation, targeting, and positioning, which help understand the following:
Customer segmentation allows you to divide potential customer groups allowing businesses to talk to them separately. It helps answer the questions:
- Are all my customers similar?
- What differentiates them from each other?
- Who is my most likely customer?
Targeting involves understanding the routines and customer behavior of these segments, allowing you to consider and choose the ideal way to speak to them. It helps answer the questions:
- Where do my customers interact with the brand?
- What’s the best time, place, medium, and format to talk to them about my brand?
Positioning helps you understand how to talk about your product/service, in order to maximize customer lifetime value. It helps answer the question:
- What type of brand message will increase and ensure brand trust?
- What type of brand message is likely to induce a purchase interaction?
Principles of segmentation, targeting, and positioning have been used for ages in the field of marketing. However with the advent of data analytics, and the creation of number-driven models like RFM, the scope of these principles has widened tremendously. Today, businesses can go beyond the above questions with the help of RFM analysis and get answers to highly specific questions such as:
- Who are my best customers?
- Which customer has the potential to buy more?
- Which customer has been churned out/has lapsed?
- Which customer can the business afford to ignore to effectively utilize budgets?
- Which customer can be converted by creating value through promotions?
- Which customer is likely to be loyal in the near future?
The RFM model allows businesses to gain key customer actionable insights, through convenient valuable insights, and frame business strategy with those insights at the heart of every decision. The model allows the business to gain perspective on what their brand means to the existing customers, helps businesses manage customer perceptions, and also translates positive sentiment into purchase opportunities.
Businesses can recognize critical customer segments like churn-risk users, and create a bespoke marketing plan, specifically designed for customer retention.
Simultaneously, a business can also use the model to maximize monetary value, the potential of active customers, by creating customized offerings, making them feel like high-value customers.
Why Does RFM Analysis Work?
The RFM model is fundamentally built using principles of data-driven marketing. Data-driven marketing has fundamentally transformed how marketing works ever since its inception, as it allows the RFM analysis of large sets of customer data like never before.
This has led to increased accuracy in understanding customers and enhanced ability to creatively customize messaging. The rise of automation in marketing technology has led to increased granularity and personalization, leading to enhanced relevance of each brand message.
Origins of RFM
RFM traces its origin back to 1995 when it was cited by Bult and Wansbeek in an issue of Marketing Science. Used in the context of direct mail, it showcased how the three criteria could be used to better estimate demand, reduce costs on printing and shipping, and lead to enhanced returns. With the rising sophistication of computing power, RFM has become easier to apply in businesses due to the computerized customer histories of today.
Applying Pareto Principle to RFM
The model is linked with the famous Pareto Principle, which says that 80% of total results are driven by the top 20% of causes. When applied to marketing, it means that 80% of your total sales are likely to come from your top 20% of customers. Regular customers will always be high contributors to business monetary value, and hence that customer segmentation is highly critical for business performance.
Role of RFM in Customer Retention
Small businesses constantly face the pressure of acquiring new customers, which defines their growth and trajectory and are prone to spending high amounts of money to acquire them. A business cannot sustain itself without customers, and while acquisition is a critical part of business strategy, customer retention plays a bigger role in ensuring high returns for the business.
Customer retention depends on customer satisfaction with the product, the service provided by the business, and the interactions the customer has with the business, hence making them feel valued.
Low churn rates are the easiest way to maintain and grow business, as it enables a reliance on customer satisfaction, and also the creation of positive word of mouth by customers. Now, with the RFM model, each segment customers can have their own customer journeys based on personalization. This helps create value and establish loyalty and trust.
RFM: Personalization and Focused Use of Marketing Budgets
The digital world is a buyer’s market, with a plethora of options available to a user at their fingertips. Brands are constantly jostling and fighting for a share of the customer’s wallet and attention. In such an atmosphere, understanding customer behavior and segmenting them into distinct groups, help businesses focus their marketing efforts on relevant customers.
With the power of social media at their fingertips to express displeasure and the ease of choosing alternatives, customer expectations regarding the quality of brand interactions are high. Hence creating relevant messaging, tailored to user behavior has become the norm.
Personalization is one of the major benefits of RFM, as it not only allows you to target different customers with varying but equally relevant messaging, but also gives businesses the ability to recognize changing patterns of user behavior through the capture of RFM data, and move the customers to other segments if required.
Through RFM, businesses can recognize and focus on converting critical customer segments like customers on the verge of churning out to becoming active customers, and also encouraging loyal customers to the brand to become ardent followers. By minimizing the waste of resources through effective targeting, RFM helps businesses utilize their marketing budgets wisely and effectively, while also increasing the overall impact of marketing on the business.
A 5-step Approach to RFM Analysis
Now that we’ve understood the benefits and basis of RFM, here are the steps involved in practically conducting RFM analysis on your customers.
1. Collection and Collation of relevant data/values.
As we’ve mentioned already, the RFM model involves the analysis of customer transaction history. The first step is to pull out the RFM data for each customer in ascending order.
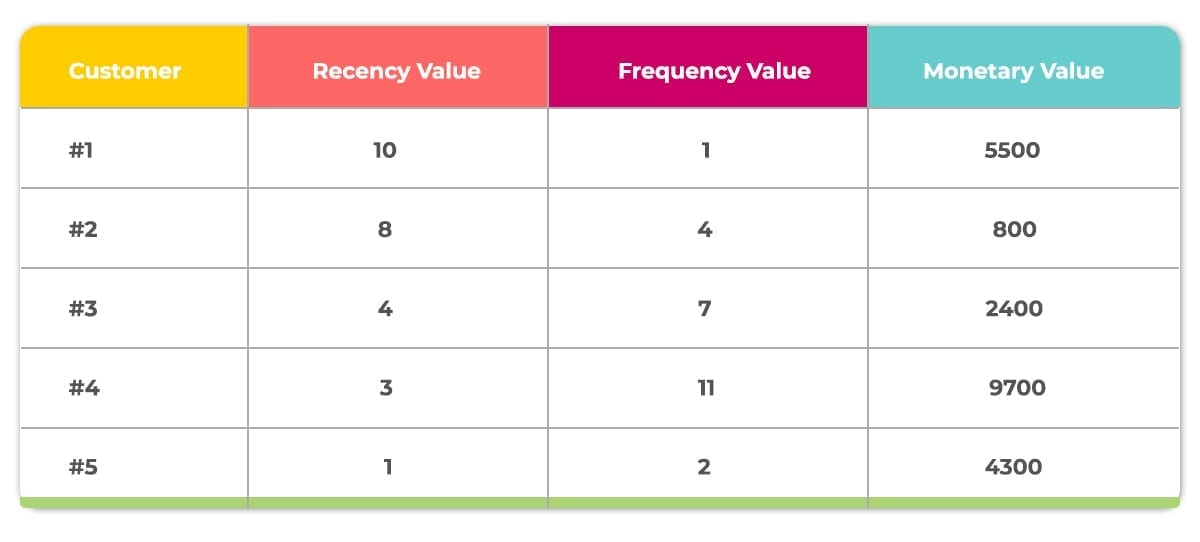
2. Setting the RFM metrics
As mentioned above, businesses need to create custom filters in order to effectively segment the customers. In order to ensure easy understanding, we will create sample RFM metrics below, but this is an important aspect that will vary based on the nature of their business.
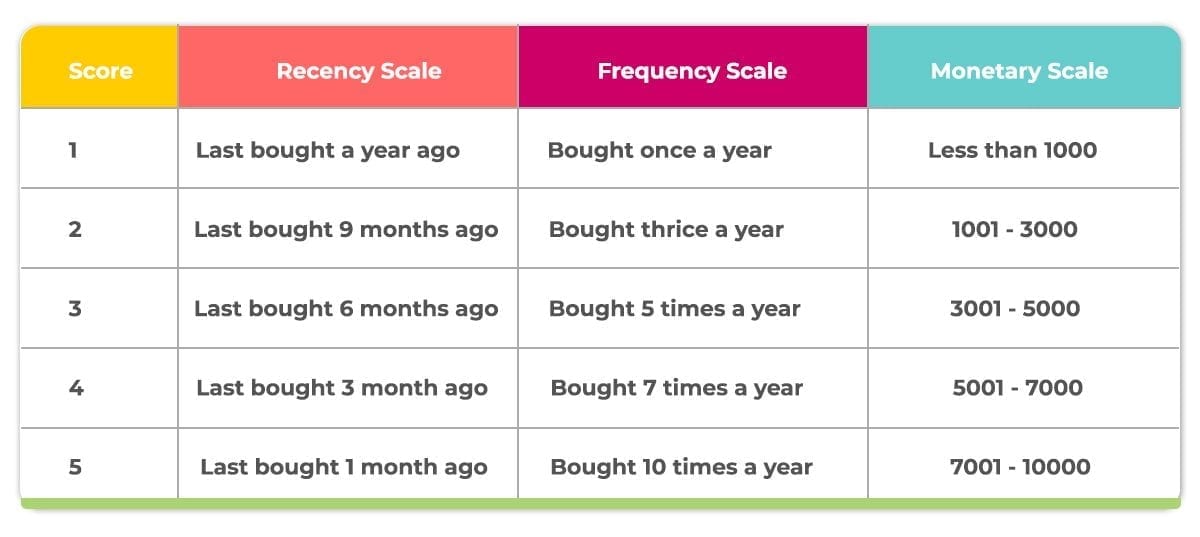
3. Assigning scores with RFM segmentation
You can now assign each customer a grade based on the table above by using RFM segmentation. By doing so, you’re converting absolute values of transactions into chunks of similar transactions, based on RFM. Now you no longer need the absolute values mentioned in brackets, and just use the score for segmentation and analysis. After assigning scores, you can create chunks of similar customers, who have identical or similar scores in the three criteria.
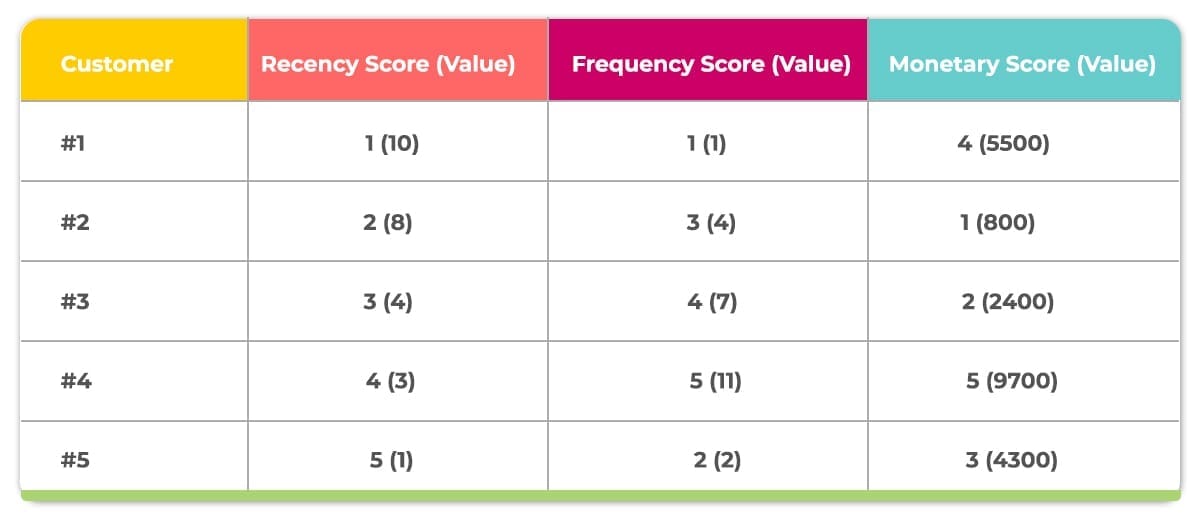
4. Labeling segments
The labels we use will be based on the differing characteristics of the three grades customers have received. As we’ve used 5 (1-5) score segments, and there are 3 criteria, there is a possibility of ((5*5*5) 125 unique segments. Businesses may or may not require 125 distinct segments and can decide the number of scoring segments required and label them, based on the nature of the business. Here are some standard labels which are used:
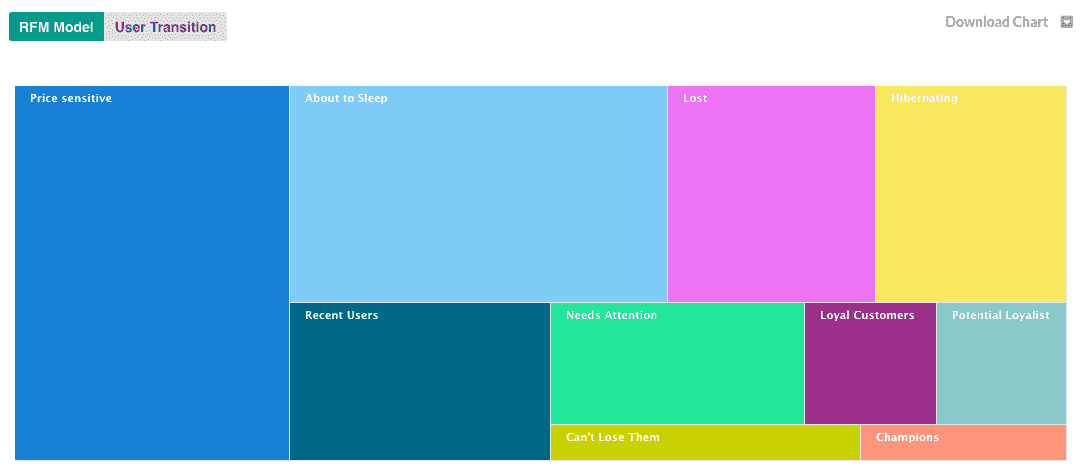
Let’s describe each of these segments in a bit more detail.
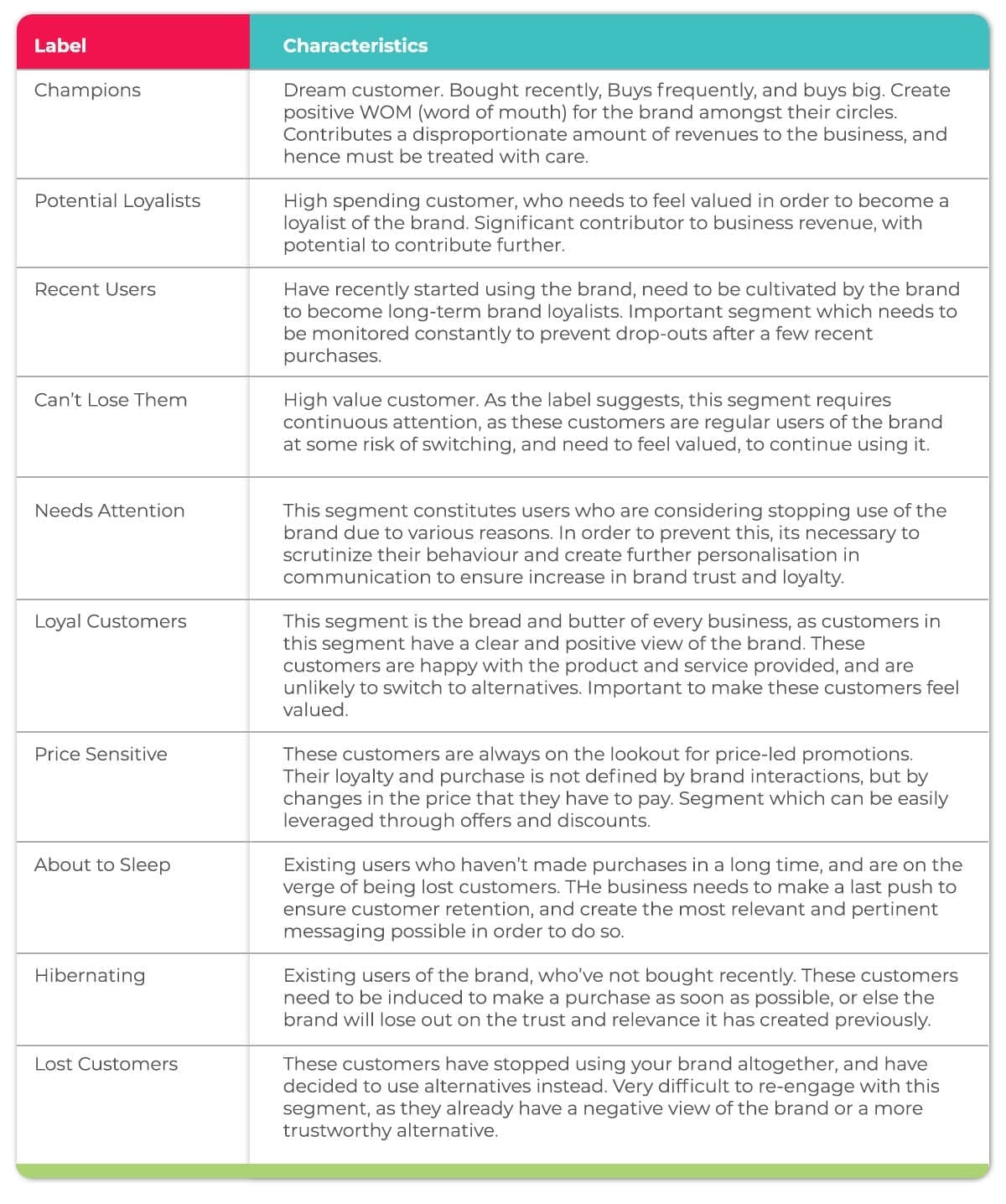
5. Creating customized strategies/tactics for relevant segments
Once businesses have segmented and labeled each customer, they can ensure personalization in all their messaging. At-risk customers can be targeted with offers, discounts, or freebies, whereas loyal customers can be provided a superior level of service in order to make them feel more valued. Recent customers can be sent information about other products that they would be interested in, whereas the Champion customer could be given greater access to products and used as a mechanism for feedback, before launching it to other customers. All of this can be done simultaneously by the business.
Alternative Models: RF, FM, And RM Models and Relevant Use Cases
Just as businesses can choose to use a varying number of score segments, they can also choose to focus on any 2 of the 3 RFM criteria, based on the nature of their business.
For example, companies with a single product can choose to focus only on the RF criteria, as that will be the easiest way to forecast demand and create messaging. When it comes to the RF criteria, most companies can use this model to gauge demand, by analyzing online search patterns as potential customers look for products online, multiple times.
Companies that sell products that are one-time purchases can choose to focus on RM criteria, as frequency would usually be fixed. Subscription-based businesses can make use of the RM model, to gauge if consumers are satisfied enough with your product, to return and make another purchase.
Companies that produce long-lasting products, can choose to focus on FM criteria, as the importance of recency would be relatively lower. Media platforms can make use of the FM criteria, as it would allow them to observe the consumption of content, and whether the customer has successfully upgraded to paying for premium content, by tracking monetary value.
Things to Remember
- Understanding the importance of RFM criteria to your business, and recognizing the importance and relevance of each, is essential to getting maximum returns from this model. This will help businesses in choosing the correct criteria, and create the right filters for segmentation.
- RFM is a model based on historical data and helps forecast future behavior based on past interactions. It is essential to remember that it can be used to target existing customers only, and helps only indirectly in acquiring new customers.
Practical Applications of RFM in Business Strategy
Media selection
Once RFM analysis is completed, there is an increased understanding of what the user needs most from your brand, and based on behavior, when are they likely to interact with you. A differentiated media strategy, combining multiple formats and mediums, for varying durations, can be created to target different segments based on their characteristics.
Messaging
RFM analysis allows you to create customized and personalized marketing messaging, and this can be used to streamline the various messages you send to a specific customer and continue sending messages of only a particular type, thereby reducing the chance of dissatisfaction or annoyance, and create higher customer satisfaction.
New launches
RFM allows you to recognize your most valuable and least valuable customers, and during the launch of a new product, the Champion customer can be engaged in a way that creates high WOM, which positively impacts product perception amongst other customers, leading to greater awareness and eventual purchase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, constant improvements in data analytics have ensured that the practical applications of models like RFM are seemingly endless. The RFM model ensures effective marketing practices in a world where creating a customer-centric experience is of utmost importance.
The RFM model, when used in conjunction with traditional models of segmentation, can help businesses visualize new and existing customers differently, and create favorable conditions to maximize customer lifetime value. Finding the right balance between focusing on new and existing customers, along with recognizing behavioral nuances within them, will help businesses create personalized customization, leading to brand trust and loyalty.







